Adding a Database to an Existing SQL Server Always On Availability Group using Backup and Restore Method.
Table of Contents
- Verify Prerequisites
- Existing Always On Availability Group
- Create Database
- Set FULL Recovery Model
- Create Tables
- Insert Sample Data
- Verify Data
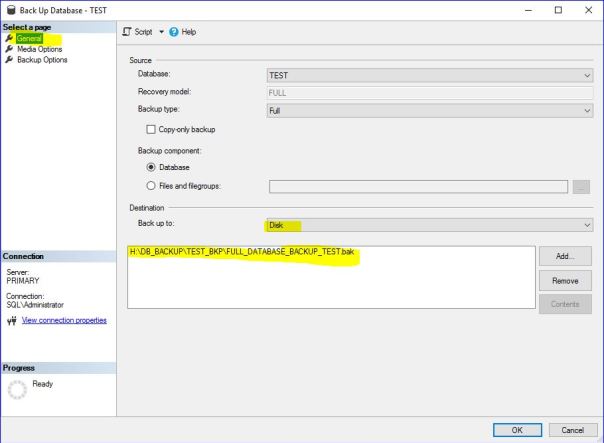
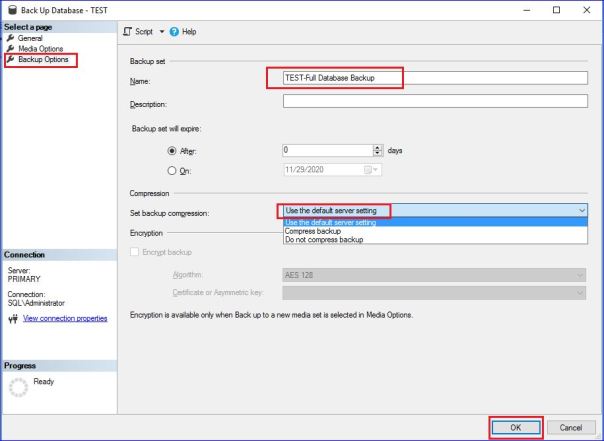
- Take Full Backup on Primary
- Transfer Backup to Secondary Replica
- Restore Database on Secondary Replica
- Add Database to Existing Availability Group
- Join Database on Secondary Replica
- Verify AG Synchronization Status
Adding a database to an existing Always On Availability Group (AG) allows the database to participate in High Availability and Disaster Recovery along with other databases in the group.
Automatic seeding streams the entire database over the AG endpoint network. Primary automatically transfers database to secondary, no need to take backup and restore manually. Please make sure grant ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP [NTICBPSQLSGA05] GRANT CREATE ANY DATABASE; to AG it self, else database will not get create automatically on secondary replica.
For large production databases (size 100 GB or more), then manual backup and restore is the preferred and more reliable method for seeding the database into the Availability Group.if you are using SEEDING_MODE = AUTOMATIC, when SQL Server detects that the database already exists on the secondary in RESTORING state, it does NOT trigger automatic seeding. Instead, it simply joins the database to the AG automatically.
if you are using SEEDING_MODE = MANUAL, you need to run the below command to join the secondary replica.ALTER DATABASE [TRDPA] SET HADR AVAILABILITY GROUP = [NTICBPSQLSGA05];
1. Verify Prerequisites
- Database must be in FULL recovery model - A full backup must exist - A transaction log backup must exist - Database must not already be part of another AG
2. Existing Always On Availability Group

3. CREATE DATABASE
USE [master];
GO
CREATE DATABASE TRDPA;
GO

4. SET FULL RECOVERY MODEL (MANDATORY FOR AG)
ALTER DATABASE TRDPA SET RECOVERY FULL;
GO
SELECT name, recovery_model_desc FROM sys.databases WHERE name = 'TRDPA';
GO

5. CREATE TABLES
USE [TRDPA]; GO -- Trade Header Table CREATE TABLE dbo.TradeHeader ( TradeID INT IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, TradeRef VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, TradeDate DATE NOT NULL, SettlementDate DATE NOT NULL, TraderName VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, DeskName VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, Status VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'PENDING', CreatedAt DATETIME2(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT SYSUTCDATETIME(), UpdatedAt DATETIME2(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT SYSUTCDATETIME(), CONSTRAINT PK_TradeHeader PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED (TradeID), CONSTRAINT CHK_Status CHECK (Status IN ('PENDING','CONFIRMED','SETTLED','CANCELLED')) ); GO -- Trade Detail Table CREATE TABLE dbo.TradeDetail ( DetailID INT IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, TradeID INT NOT NULL, Instrument VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, AssetClass VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, Quantity DECIMAL(18,4) NOT NULL, Price DECIMAL(18,6) NOT NULL, Notional AS (Quantity * Price) PERSISTED, Currency CHAR(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'USD', Direction CHAR(1) NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT PK_TradeDetail PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED (DetailID), CONSTRAINT FK_TradeDetail_Header FOREIGN KEY (TradeID) REFERENCES dbo.TradeHeader(TradeID), CONSTRAINT CHK_Direction CHECK (Direction IN ('B','S')) ); GO -- Audit Log Table CREATE TABLE dbo.AuditLog ( AuditID INT IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, TradeID INT NOT NULL, ActionType VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, ActionBy VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL DEFAULT SYSTEM_USER, ActionAt DATETIME2(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT SYSUTCDATETIME(), OldStatus VARCHAR(20) NULL, NewStatus VARCHAR(20) NULL, Remarks NVARCHAR(500) NULL, CONSTRAINT PK_AuditLog PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED (AuditID) ); GO

6. INSERT SAMPLE DATA
-- Trade Headers
INSERT INTO dbo.TradeHeader (TradeRef, TradeDate, SettlementDate, TraderName, DeskName, Status)
VALUES
('TRD-2026-00001', '2026-03-01', '2026-03-03', 'John Smith', 'Equities', 'CONFIRMED'),
('TRD-2026-00002', '2026-03-03', '2026-03-05', 'Sarah Connor', 'Fixed Income', 'SETTLED'),
('TRD-2026-00003', '2026-03-05', '2026-03-07', 'Mike Johnson', 'FX', 'PENDING'),
('TRD-2026-00004', '2026-03-07', '2026-03-11', 'Emily Davis', 'Equities', 'CONFIRMED'),
('TRD-2026-00005', '2026-03-10', '2026-03-12', 'Raj Patel', 'Commodities', 'PENDING'),
('TRD-2026-00006', '2026-03-10', '2026-03-12', 'Lisa Wang', 'FX', 'CANCELLED'),
('TRD-2026-00007', '2026-03-11', '2026-03-13', 'Tom Harris', 'Fixed Income', 'PENDING'),
('TRD-2026-00008', '2026-03-11', '2026-03-13', 'Anna Brown', 'Equities', 'CONFIRMED');
GO
-- Trade Details
INSERT INTO dbo.TradeDetail (TradeID, Instrument, AssetClass, Quantity, Price, Currency, Direction)
VALUES
(1, 'AAPL US Equity', 'Equity', 1000.0000, 178.500000, 'USD', 'B'),
(1, 'MSFT US Equity', 'Equity', 500.0000, 415.250000, 'USD', 'B'),
(2, 'US10Y Treasury', 'Fixed Income', 2000.0000, 98.750000, 'USD', 'S'),
(3, 'EUR/USD', 'FX', 1000000.0000, 1.085000, 'USD', 'B'),
(4, 'TSLA US Equity', 'Equity', 300.0000, 172.900000, 'USD', 'S'),
(4, 'NVDA US Equity', 'Equity', 200.0000, 875.600000, 'USD', 'B'),
(5, 'Gold Futures Jun26', 'Commodity', 50.0000, 2185.400000, 'USD', 'B'),
(6, 'GBP/USD', 'FX', 500000.0000, 1.270000, 'USD', 'S'),
(7, 'US2Y Treasury', 'Fixed Income', 1500.0000, 99.125000, 'USD', 'B'),
(8, 'AMZN US Equity', 'Equity', 400.0000, 178.320000, 'USD', 'B');
GO
-- Audit Log
INSERT INTO dbo.AuditLog (TradeID, ActionType, OldStatus, NewStatus, Remarks)
VALUES
(1, 'STATUS_CHANGE', 'PENDING', 'CONFIRMED', 'Confirmed by risk desk'),
(2, 'STATUS_CHANGE', 'PENDING', 'CONFIRMED', 'Confirmed by risk desk'),
(2, 'STATUS_CHANGE', 'CONFIRMED', 'SETTLED', 'Settlement confirmed by ops'),
(6, 'STATUS_CHANGE', 'PENDING', 'CANCELLED', 'Cancelled - counterparty default');
GO
7. VERIFY DATA
SELECT
h.TradeRef,
h.TradeDate,
h.TraderName,
h.DeskName,
h.Status,
d.Instrument,
d.Direction,
d.Quantity,
d.Price,
d.Notional,
d.Currency
FROM dbo.TradeHeader h
JOIN dbo.TradeDetail d
ON h.TradeID = d.TradeID
ORDER BY h.TradeDate, h.TradeRef;
GO

8. FULL BACKUP on Primary
A Full Backup contains data pages and enough transaction log to make the database consistent, but it does NOT include all transaction log activity after the backup started.
Therefore we take a separate transaction log backup to maintain the log chain.
BACKUP DATABASE TRDPA TO DISK = 'K:\Microsoft SQL Server\TRDPA\TRDPA_full.bak'; GO BACKUP LOG TRDPA TO DISK = 'K:\Microsoft SQL Server\TRDPA\TRDPA_log.trn'; GO


9. Transfer Backup to Secondary Replica(s)
Shared backup location: //Nticbpsqlsgv01/trdpa
Copy backup files from the shared location to secondary servers.


10. Restore Database on Secondary Replica(s)
10.1 Restore on Secondary Replica 1
RESTORE DATABASE TRDPA FROM DISK = 'K:\Microsoft SQL Server\TRDPA\TRDPA_full.bak' WITH NORECOVERY; RESTORE LOG TRDPA FROM DISK = 'K:\Microsoft SQL Server\TRDPA\TRDPA_log.trn' WITH NORECOVERY;


10.2 Restore on Secondary Replica 2
-- Restore Database RESTORE DATABASE TRDPA FROM DISK = 'K:\Microsoft SQL Server\TRDPA\TRDPA_full.bak' WITH NORECOVERY; -- Restore LOG RESTORE LOG TRDPA FROM DISK = 'K:\Microsoft SQL Server\TRDPA\TRDPA_log.trn' WITH NORECOVERY;

11. ADD DATABASE TO EXISTING AG (Primary Server)
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP [NTICBPSQLSGA05] ADD DATABASE [TRDPA];

12. Join Database on Secondary Replica(s)
When SQL Server detects that the database already exists on the secondary in RESTORING state, it does NOT trigger automatic seeding. Instead, it simply joins the database to the AG automatically.You only need to run the below command when using Manual Seeding.
ALTER DATABASE [TRDPA] SET HADR AVAILABILITY GROUP = [NTICBPSQLSGA05];
GO


13. VERIFY AG SYNC STATUS
SELECT
ag.name AS ag_name,
ar.replica_server_name,
db.database_name,
drs.synchronization_state_desc,
drs.synchronization_health_desc,
drs.log_send_queue_size,
drs.redo_queue_size,
drs.last_commit_time
FROM sys.availability_groups ag
JOIN sys.availability_replicas ar
ON ag.group_id = ar.group_id
JOIN sys.dm_hadr_availability_replica_states rs
ON ar.replica_id = rs.replica_id
JOIN sys.dm_hadr_database_replica_states drs
ON rs.replica_id = drs.replica_id
JOIN sys.availability_databases_cluster db
ON drs.group_database_id = db.group_database_id
WHERE db.database_name = 'TRDPA'
ORDER BY ar.replica_server_name;
GO


Caution: Your use of any information or materials on this website is entirely at your own risk. It is provided for educational purposes only. It has been tested internally, however, we do not guarantee that it will work for you. Ensure that you run it in your test environment before using.
Thank you,
Rajasekhar Amudala
Email: br8dba@gmail.com
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/rajasekhar-amudala/